What is Ultrasound ?

Professional explanation
Ultrasound imaging is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves (typically 2-1 5 MHz).
These sound waves travel through the body and reflect off different structures.
The returning echoes are used to create real-time images that help diagnose a wide range of conditions.
Simple explanation
Ultrasound lets doctors “see" inside the body using sound waves-like creating a picture from echoes.
It's similar to giving the doctor both “ears" and “eyes" to look at the liver, heart, uterus, blood vessels, and more.
Why is Ultrasound One of the Most Popular lmaging Methods Today?
1️⃣ Non-invasive & Safe
No needles, no radiation - safe for pregnant women and children.
2️⃣ Real-time lmaging
Live images instantly, doctors can make on-the-spot decisions.
3️⃣ Versatile
Used for many body areas: abdomen, heart, OB/GYN, vessels...
4️⃣ Fast & convenient
Quick scan process with no complex preparation needed.
5️⃣ Affordable
Lower cost than CT or MRl, ideal for wide accessibility.
🔵 lmaging capabilities depend on the ultrasound system (main unit), while probe types (e.g. linear or convex) refer to the transducer's array design.
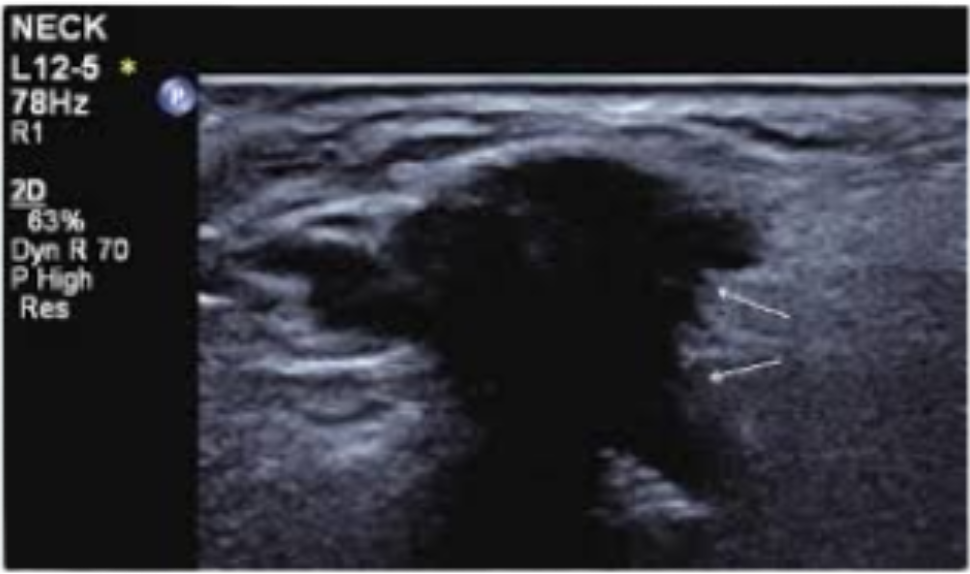
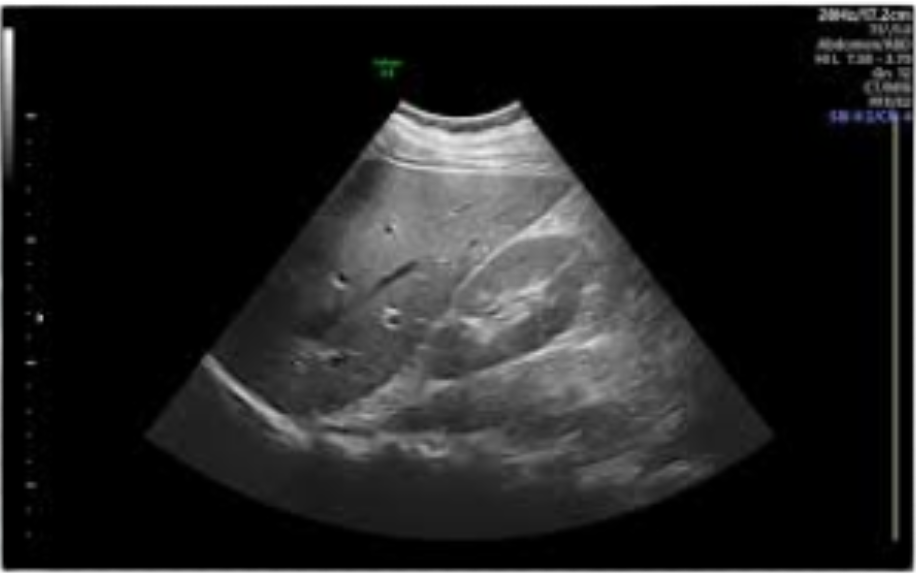
📷 Ultrasound lmaging Modes
B-Mode (2D):
Standard grayscale imaging to display anatomical structures. Widely used in general diagnostics.
M-Mode:
Captures motion over time, ideal for assessing moving structures (e.g., heart valves).
Doppler Modes:
Measures blood flow speed and direction (Color Doppler, Pulsed Wave, Continuous Wave).
Color Doppler:
Displays color-coded blood flow over anatomical images for vascular assessments.
3D/4D Ultrasound:
Provides volumetric (3D) or real-time moving (4D) images-commonly used in obstetrics.
Elastography:
Visualizes tissue stiffness, helpful for tumor evaluation and liver fibrosis detection.

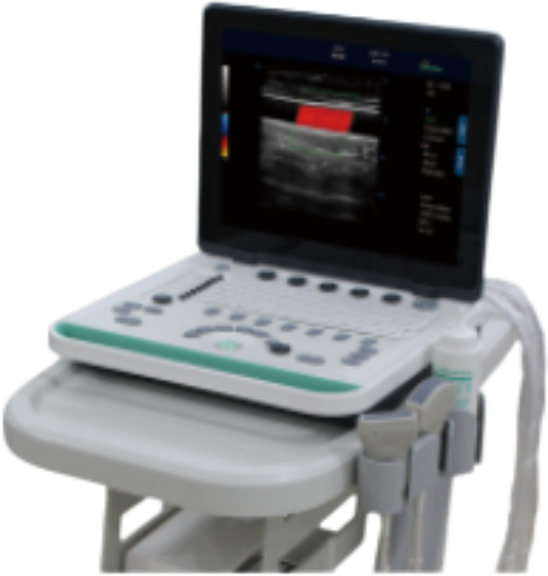
Console Ultrasound Machine

Portable Ultrasound
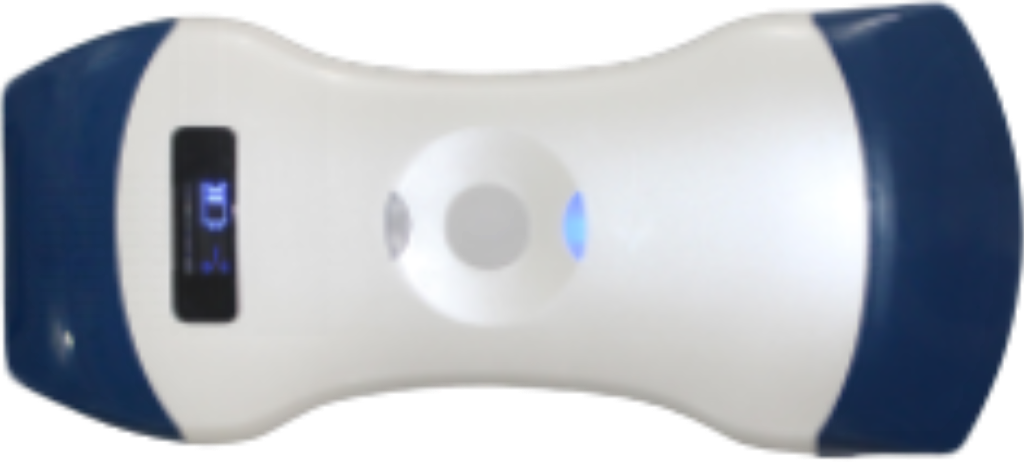 MG-CCL02
MG-CCL02
Wireless Ultrasound